Rollbacks in blockchain explained
In blockchain, a rollback refers to reversing its history to counter a disastrous event, such as big hacks threatening to disrupt the ecosystem, the discovery of critical protocol bugs or centralization risks of network integrity.
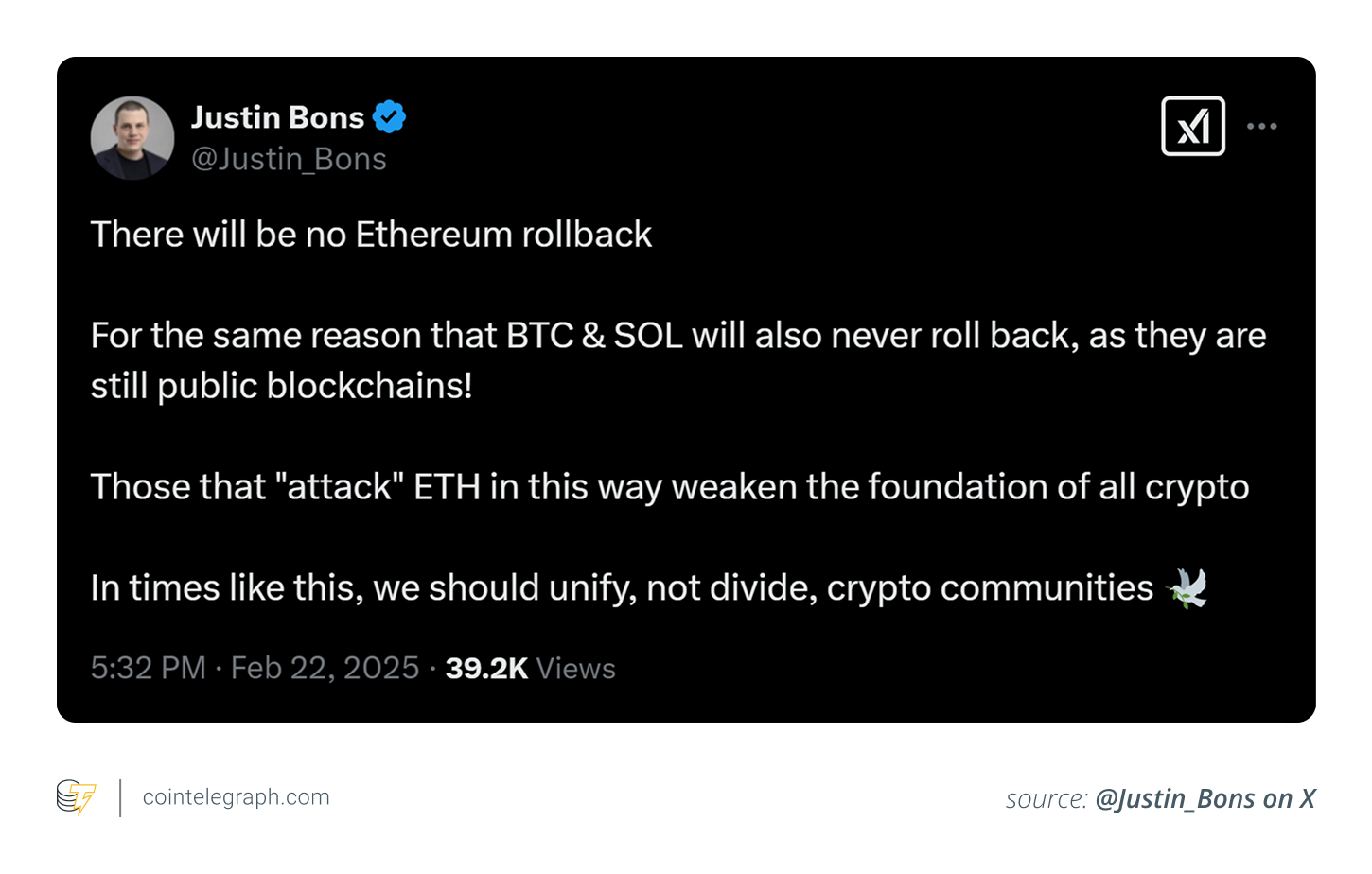
The Bybit hack, which resulted in a staggering $1.46 billion loss, has triggered a demand regarding a rollback of affected transactions on Ethereum.
In a Feb. 22 X Spaces, Bybit CEO Ben Zhou adopted a more neutral position when asked about supporting an Ethereum rollback.
“I’m not sure it should be a decision made by one person. In line with the spirit of blockchain, it might be better to have a voting process to determine what the community wants, but I’m uncertain,” Zhou said.
Still, Jan3 CEO Samson Mow commented in a Feb. 22 X post: “I fully support rolling back Ethereum’s chain (again) so the stolen ETH is returned to Bybit and also to prevent the North Korean government from using those funds to finance their nuclear weapons program.”
Similarly, BitMEX co-founder Arthur Hayes tagged Ethereum founder Vitalik Buterin, urging him to “advocate for rolling back the chain,” in a Feb. 22 X post.
While viewed as a last resort, this idea challenges the fundamental principles of blockchain — immutability and decentralization.
A rollback is theoretically possible but highly debatable, particularly on a large blockchain like Ethereum. Ethereum has evolved into an expansive ecosystem with several layer-2 solutions and numerous decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
A rollback in blockchain can be achieved through a soft fork or hard fork, both of which involve modifying the blockchain’s history.
- Soft fork: A less drastic change that is backward-compatible, meaning the updated version is still valid on the old chain. It could be implemented without requiring a total consensus.
- Hard fork: A more drastic change where the blockchain splits into two, with the new version being incompatible with the previous one. This requires widespread consensus and could lead to a permanent division in the network.
In both cases, reversing transactions on such a significant ecosystem would require overwhelming consensus from the network participants, making it an extremely complex and controversial decision with potentially unexpected and equally calamitous fallouts.
In addition to hard and soft forks, a blockchain patch is another method of rollback. It involves a specific fix for an issue where the blockchain’s history is “rolled back” to a previous state, effectively reversing certain transactions or events.
Did you know? Hackers stole 120,000 BTC in the 2016 Bitfinex hack. If you calculate the value of the stolen BTC in 2025, it would be more than $8 billion.
Bybit hack explained
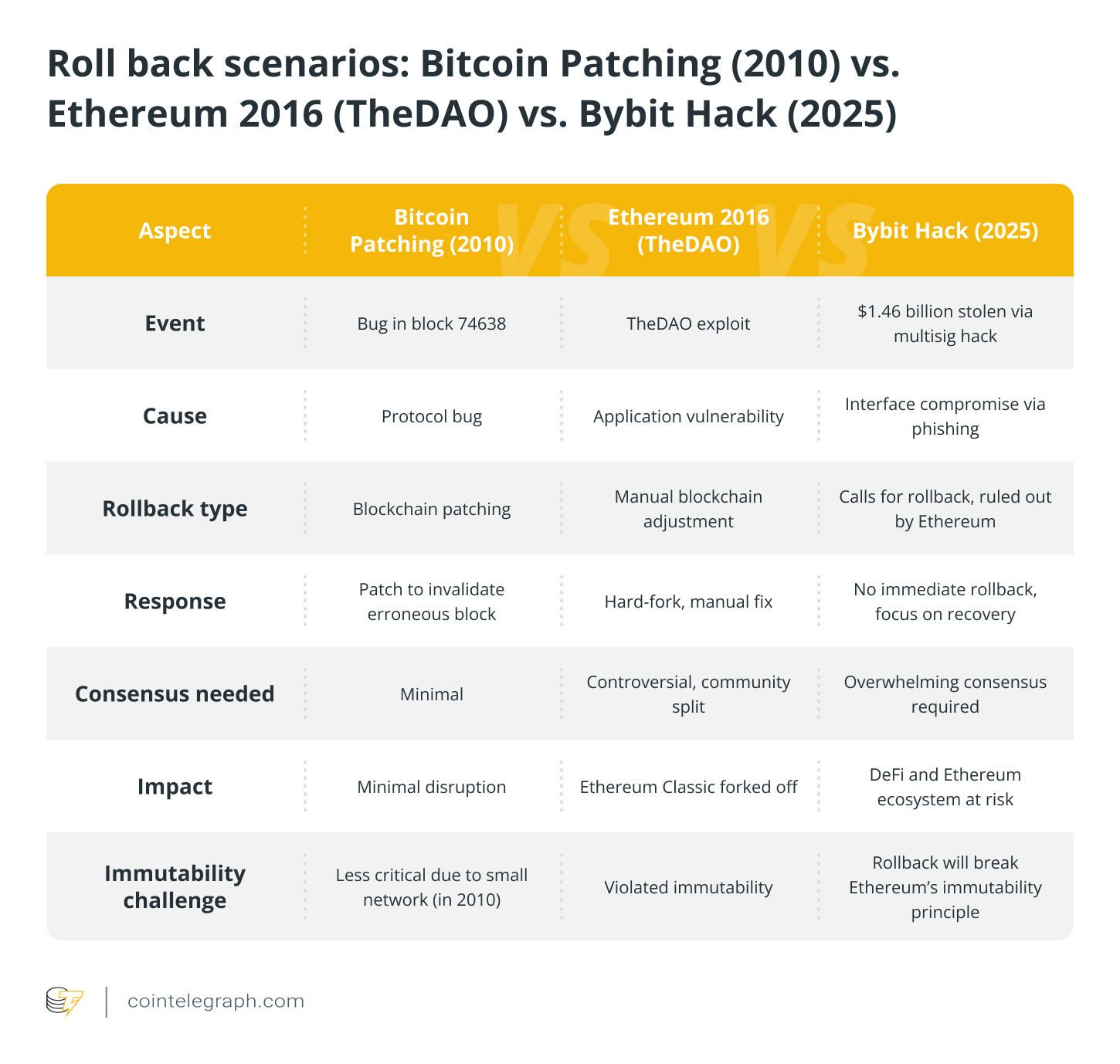
On Feb. 21, 2025, hackers stole around $1.46 billion in crypto from Bybit. Hackers used specifically developed malware to trick Bybit’s multisignature system into approving fraudulent transactions and sending funds to the attackers.
The theft was linked to North Korea’s Lazarus Group, infamous for breaching crypto platforms and laundering stolen assets through complex blockchain transactions.
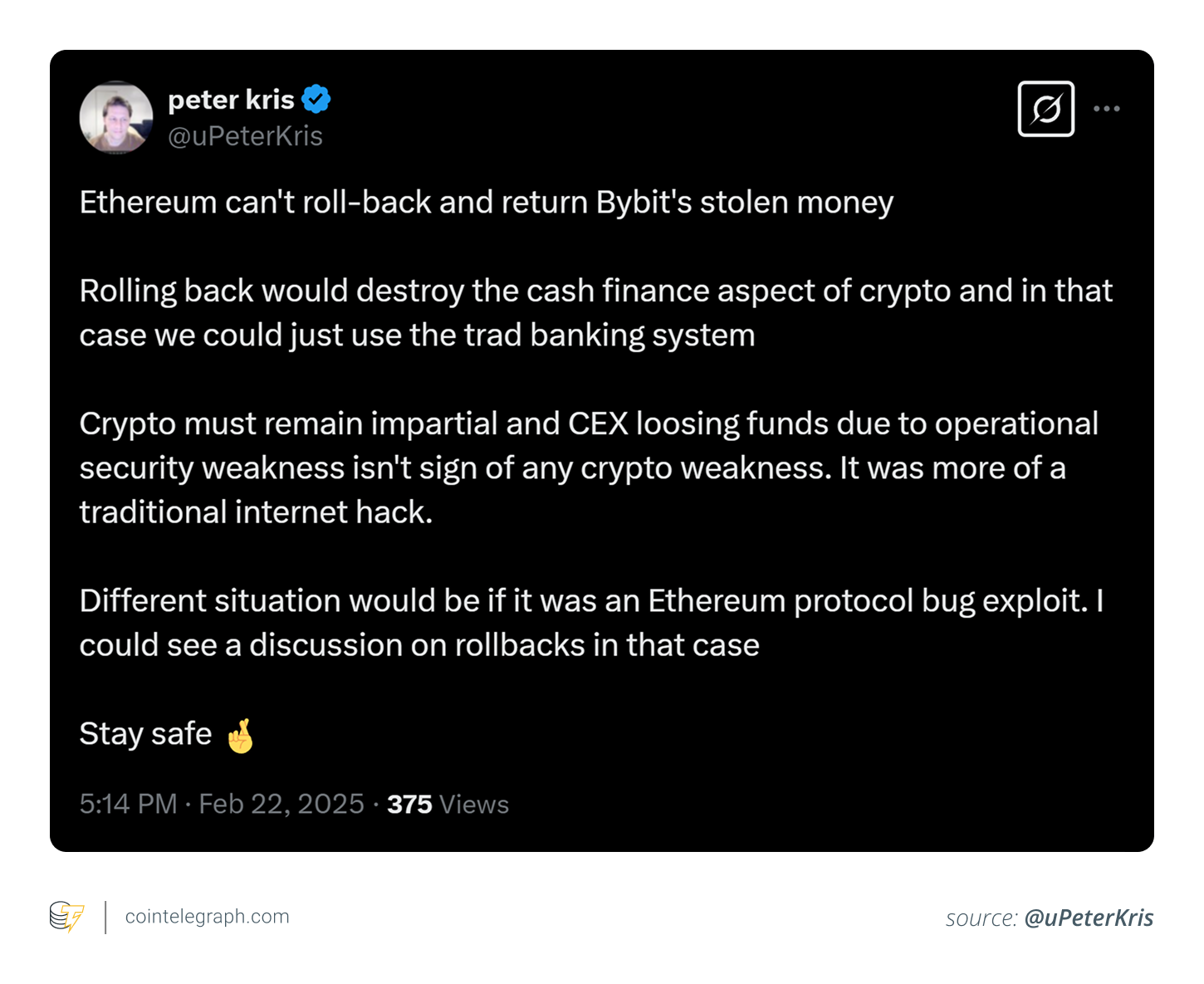
The hackers converted stolen tokens like stETH and cmETH into Ether (ETH) on decentralized exchanges (DEXs). They then swapped large amounts of ETH for Bitcoin (BTC) and Dai (DAI). The attack was executed by tricking Bybit executives with a fake interface. The crypto exchange has launched a recovery bounty, offering up to 10% of recovered funds to anyone who helps retrieve the stolen crypto.
The attackers used phishing tactics to compromise Bybit’s cold wallet signers, replacing the multisignature contract with a malicious one. The “blind signature” tactics made it hard for the users to detect they were interacting with a fake interface while doing a routine transfer from Bybit’s cold wallet to a hot wallet.
It enabled the transfer ownership action that passed control of the entire multisignature process to the hackers. As a result, the hackers redirected about 401,000 ETH, worth nearly $1.46 billion, to their own addresses.
Roadblocks in rolling back Ethereum transactions
Built-in immutability is a significant hindrance to reversing Ethereum transactions. This key feature ensures records cannot be changed at the will of any particular authority, which conflicts with calls for rollbacks after events like the Bybit hack.
Reversing transactions would also erode user trust, disrupt the DeFi ecosystem and weaken Ethereum’s credibility. Moreover, Ethereum has grown into a vast network since its inception, making a rollback technically infeasible.
Let’s understand the roadblocks in a bit more detail:
Immutable design
Immutability is a fundamental principle of blockchain, ensuring that past transactions remain unaltered. Along with decentralization, this is a major advantage of Web3 over Web2 centralized systems. Rolling back transactions would directly challenge this core tenet.
When there is an uproar demanding a rollback, a blockchain network faces a dilemma — should network survival take precedence over a basic tenet or should immutability be upheld despite potential losses?
Following the Bybit hack, Ethereum ruled out a rollback, citing technical infeasibility. This suggests that the blockchain has chosen immutability, prioritizing a founding principle of blockchain over reversing transactions propelled by an event. This decision strengthens Ethereum’s ecosystem and sets a precedent for other blockchain networks.
Trust and ecosystem stability
Ethereum’s strength lies in the trust users place in its decentralized infrastructure. A rollback would disrupt that trust, raising concerns about the reliability of crypto wallets, exchanges and DeFi platforms — in short, anything built on Ethereum.
Since Ethereum acts as a platform for DeFi and crosschain settlements, altering its transaction history could have widespread consequences, affecting businesses, payment networks and investors.
Beyond technical hurdles, rollbacks would create uncertainty, weakening Ethereum’s credibility and disrupting adoption. Cultivating stability and trust helps Ethereum ensure its long-term resilience in the evolving crypto landscape.
Did you know? A critical flaw in the Parity Wallet’s smart contract code allowed attackers to steal $30 million in ETH, exploiting a vulnerability in its multisignature functionality.
Technical infeasibility
Ethereum’s ecosystem has evolved significantly since 2016. With DeFi and crosschain bridges, stolen funds can be quickly moved, exchanged or used as collateral, making them difficult to trace. For instance, stolen assets could be swapped on a decentralized exchange, used in lending platforms and then transferred to another blockchain.
This high level of connectivity makes reversing transactions extremely complex. Even if a rollback were socially accepted, it would create widespread disruptions. Transactions with offchain effects, such as exchange trades or asset redemptions, cannot be undone, leading to potential chaos.
While it once managed a rollback, Ethereum’s interconnected system and reliance on onchain and offchain settlements make it nearly impossible today.
Origins of blockchain rollback
The idea of a blockchain “rollback” dates back to 2010, less than two years after Bitcoin’s launch, when block 74638 ended up minting 184 billion BTC because of a software flaw. To resolve this, Satoshi Nakamoto released a patched version of the Bitcoin client, invalidating these transactions.
With this action, Nakamoto reverted the blockchain to block 74637, discarding the affected chain. Within a day, the revised chain gathered sufficient proof-of-work to regain its status as the main chain. The corrected version eventually included all legitimate transactions from the discarded chain.
While the first-ever rollback was successful, Bitcoin’s network was significantly less complex at the time. Its mining difficulty was vastly less than today’s, and the BTC/USD price hovered around $0.07. This rollback was possible because the error was at the protocol level, and Bitcoin’s user base was relatively small, which allowed for quick adoption of the new client software.
Did Ethereum’s 2016 The DAO hack spark a blockchain rollback?
In 2016, Ethereum faced a crisis often confused with a blockchain rollback. The decentralized application, The DAO, held about 15% of ETH at the time but was exploited by a hacker who drained the funds. Unlike Bitcoin’s 2010 rollback, this wasn’t a protocol issue, as Ethereum itself functioned correctly; the vulnerability existed within the application built on top of it.
Luckily, The DAO had a one-month freeze before withdrawals, giving developers time to act. However, because the app developers couldn’t fix the issue, Ethereum’s core developers had to intervene by manually altering the blockchain’s history. This “extraordinary state change” adjusted The DAO’s balance directly, bypassing standard Ethereum transaction protocols.
The fix sparked controversy, splitting the Ethereum community. Some miners rejected the update, continuing the original chain, which is now Ethereum Classic, while the upgraded chain became Ethereum. The incident was unique because the error was at the application level, and the funds were frozen, preventing the hacker from moving the money and allowing coordination for a software update.
Did you know? In 2014, Mt. Gox went bankrupt after losing 850,000 BTC, which made up around 7% of all Bitcoin at the time.
Bybit hack – An overview from Ethereum’s perspective
Unlike Bitcoin’s overflow bug or TheDAO exploit, the Bybit hack originated from a compromised interface rather than a flaw in Ethereum’s protocol or its multisignature application. The attack compromised the interface, making it look legitimate, and the executives ended up executing unintended actions.
Technically, the Bybit hack is a different case than the previous instances, which were on the protocol layer and the application layer, respectively.
Easy movement of funds
Moreover, in TheDAO incident, the stolen funds were frozen for a month, allowing time for community intervention. In the Bybit hack, the attackers could move funds instantly, eliminating any opportunity for a response by the developers. Even if Ethereum developers attempted to freeze the funds, the hackers could simply move them elsewhere, creating an endless cat-and-mouse game.
Evolution of Ethereum
Ethereum of 2025 is drastically different from the same blockchain in 2016. Today’s Ethereum ecosystem is highly interconnected through DeFi applications and crosschain bridges. L2 solutions like Polygon and Arbitrum add even more complexity, making recovery efforts nearly impossible.
The impracticality of a hard fork
While Bitcoin could do blockchain patching 15 years ago, Ethereum’s vast and interlinked financial system makes this unfeasible today. Even if the community approved a hard fork, the hacker would have moved funds before implementation, rendering it ineffective.
Immutable protocol culture
Ethereum community culture has changed over time, embracing immutability and resisting non-standard state changes even in extreme cases. At present, any proposal of a hard fork in Ethereum to do away with the hack is unlikely to get the community’s approval.
Blind sign attacks – The way out
Attacks combining blind signing with malware are among the fastest-growing threats in crypto. These are not operational errors but advanced, highly targeted attacks that put both individuals and organizations at risk. Signing processes rely on software interfaces that interact with decentralized apps (DApps), creating vulnerabilities involving fake interfaces.
According to a researcher called pcaversaccio, Lazarus exploited this vulnerability by replacing Bybit’s multisignature implementation with tactics that used Ethereum’s delegatecall function. The hackers abused this low-level command, which is meant for contract upgrades.
Lazarus used this function to manipulate the multisig contract’s memory, gaining control over the funds. They executed the attack using custom malware designed for this breach and these particular signers.
To mitigate such risks, developers must rethink security strategies to deny hackers using backdoor tactics. Similarly, users should implement timelocks on their wallets to delay unauthorized changes.
Because hardware wallets lose their effectiveness if transactions are signed on compromised devices, ensuring the security of the signing environment becomes crucial. Implementing timelocks adds an extra layer of protection by preventing any changes to the wallet’s configuration within a specified time window. This limitation can disrupt an attacker’s ability to execute a hack, as it restricts their access and manipulations during the critical period.

















